Rooftop collector: on top of a sloped roof. Collectors of width 0.4m-0.5m can be installed on a sloped roof facing the sun, with receivers at horizontal direction. For such a setup, the height of the collectors above the roof can be limited to 20cm or less, which is very reasonable.
With a receiver tube of diameter 8-10mm, the smallest collector of width about 0.5m can reach a linear concentration ratio of about 50 times. This is an optimal ratio for residential applications where the working temperature should not exceed 250°C. Collectors can operate with high efficiency at this setup.
Wallfront collector: in front of a vertical wall facing the sun. Lines of collectors of width about 0.5m with horizontal receivers can be installed on the wall. An example is to install one line of collectors just below the base line of windows. Collectors can also be hooked on the outside of the balustrade of a balcony.
Esthetics may become a major attacking angle against this kind of installation. However, parabolic solar collectors are not more ugly than the omnipresent satellite dishes.
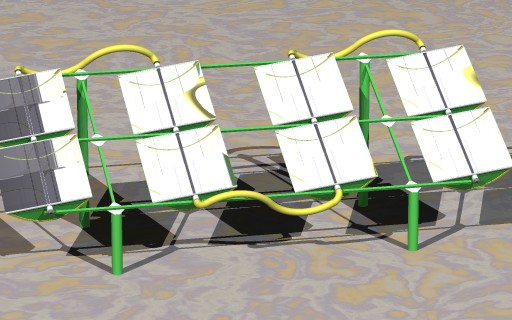
On top of a flat roof or a piece of unused flat land. This can be done using chassis of various sizes, as shown below, with either tilted or horizontal collectors. Boxes of width about 1m can be used for most of the cases.

|
|
As the collector boxes are individually tracked, there is no need to prepare the ground, nor to align the chassis and the boxes in the installation. The only requirement is that the chassis does not vibrate too much under normal wind conditions, and does not fly away under strong wind.
Elevated installation on a piece of land normally used for other purposes. This is exactly as above, but with bigger chassis and taller legs. The solar arrays can thus be installed a few meters above the ground, leaving the space below for its normal activities.
One example is parking lot. This is very suitable for solar installations, as cars have limited height. One has only to take care to reinforce the legs, so that if accidentally hit by a car, they will not collapse.
Some well exposed wide roads can be used in the same way, either highway or railway. But fluid collection is less obvious in such cases.
Other examples include spaces above a swimming pool, a pond, lawns, railway stations, a landfill, and so on.
Large scale installations on well-insulated desert lands. This is industrial exploitation for electricity generation, water desalination and production of chemical fuels. The field needs not to be very flat, and the installation can be done to leave the local ecosystem on the ground almost intact.
Bare rocky mountain slopes facing the sun, preferably not too steep.
Floating installation on a water surface. For example, the lake of a dam. This may be a very economical solution.
Mobile installation on a not-frequently-used sporting ground.